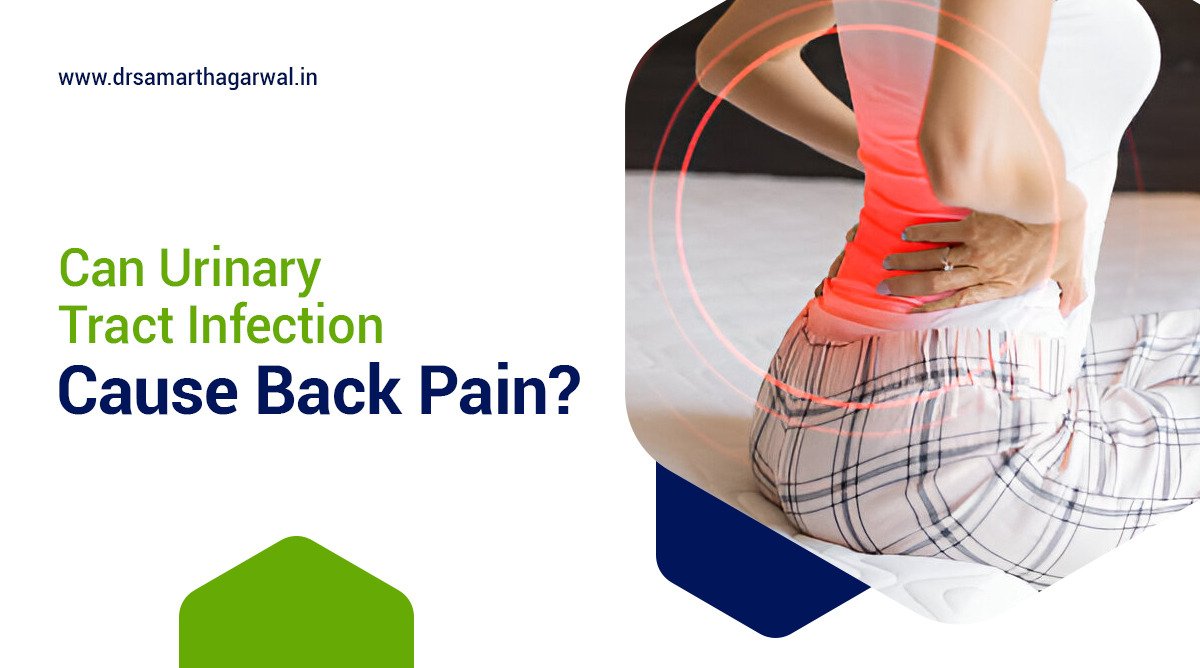
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common bacterial infections that can affect various parts of the urinary system, including the bladder, urethra, and kidneys. While UTIs are typically associated with symptoms such as frequent urination and burning sensations, many people wonder if these infections can also cause back pain. This article will explore the relationship between UTIs and back pain, as well as discuss treatment options and preventive measures.
Can back pain be a symptom of a UTI?
Yes, UTI can cause back pain. Back pain can indeed be a symptom of a urinary tract infection, particularly when the disease has spread to the kidneys. Lower back pain is often associated with UTIs that have progressed beyond the bladder. Bacteria entering the urinary system and traveling upwards can infect the ureters and kidneys, causing inflammation and discomfort. This type of infection, known as pyelonephritis or a kidney infection, can result in pain in the lower back, sides, or groin area.
According to Rosen, J. M., & Klumpp, D. J. (2014). Mechanisms of pain from urinary tract infection. International journal of urology, UTIs can cause transient pelvic pain, but certain E. coli strains lacking O-antigen can lead to chronic pelvic pain, which may persist long after the infection clears. This chronic pain is associated with central sensitization and can mimic symptoms of interstitial cystitis, suggesting a potential link between UTIs and chronic back pain.
It’s important to note that not all UTIs cause back pain, and not all back pain is indicative of a UTI. However, suppose you experience back pain along with other common UTI symptoms such as frequent urination, burning sensation while urinating, cloudy or bloody urine, and a strong urge to urinate. In that case, it may be a sign that the infection has spread to your kidneys. In such cases, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly, as kidney infections can lead to more severe complications if left untreated.
How can a person treat back pain caused by a UTI?
Treating back pain caused by a urinary tract infection primarily involves addressing the underlying infection. The most common and effective treatment for UTIs is a course of antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare professional. The type and duration of antibiotic treatment will depend on the severity of the infection and the specific bacteria causing it. It’s essential to complete the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve, to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
In addition to antibiotics, there are several measures that can help alleviate back pain and other UTI symptoms. Drinking plenty of water can help flush out bacteria from the urinary system and reduce discomfort. Some people find relief by using a heating pad on the affected area or taking over-the-counter pain relievers. While cranberry juice is often touted as a natural remedy for UTIs, its effectiveness is debated. However, maintaining good hygiene practices, such as wiping from front to back after using the bathroom, can help prevent future infections.
Where does a UTI hurt in your back?
When a urinary tract infection causes back pain, it typically manifests in the lower back region. This pain is often described as a dull ache or a more intense, sharp sensation in the area just below the rib cage, on one or both sides of the spine. The discomfort may extend to the sides of the body, particularly in the area where the kidneys are located. Some individuals may also experience pain in the upper back, although this is less common.
The location of the pain can provide clues about the extent of the infection. Lower back pain is often associated with infections that have spread to the kidneys, while pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area may indicate a bladder infection. It’s important to note that the intensity and exact location of the pain can vary from person to person, and some individuals may experience discomfort in multiple areas simultaneously.
What does it feel like when a UTI spreads to your kidneys?
When a urinary tract infection spreads to the kidneys, the symptoms can become more severe and may include a range of uncomfortable sensations. In addition to lower back pain, individuals may experience a high fever, often accompanied by chills and shaking. Nausea and vomiting are also common symptoms of a kidney infection, as well as fatigue and general malaise. The pain associated with a kidney infection is typically more intense than that of a lower UTI and may be constant or come in waves.
Other signs that a UTI has spread to the kidneys include increased urinary frequency and urgency, often with little urine output. The urine may appear cloudy, dark, or bloody, and there may be a strong, unpleasant odor. Some people also report experiencing confusion or mental fogginess when the infection reaches the kidneys. If you suspect that your UTI has progressed to a kidney infection, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention, as this condition can lead to serious complications if left untreated.

If you’re experiencing back pain along with symptoms of a urinary tract infection (UTI), it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional. Contact Dr. Samarth Agarwal if you have any questions or concerns about your urinary health and how it may relate to back pain. Your well-being is a priority!