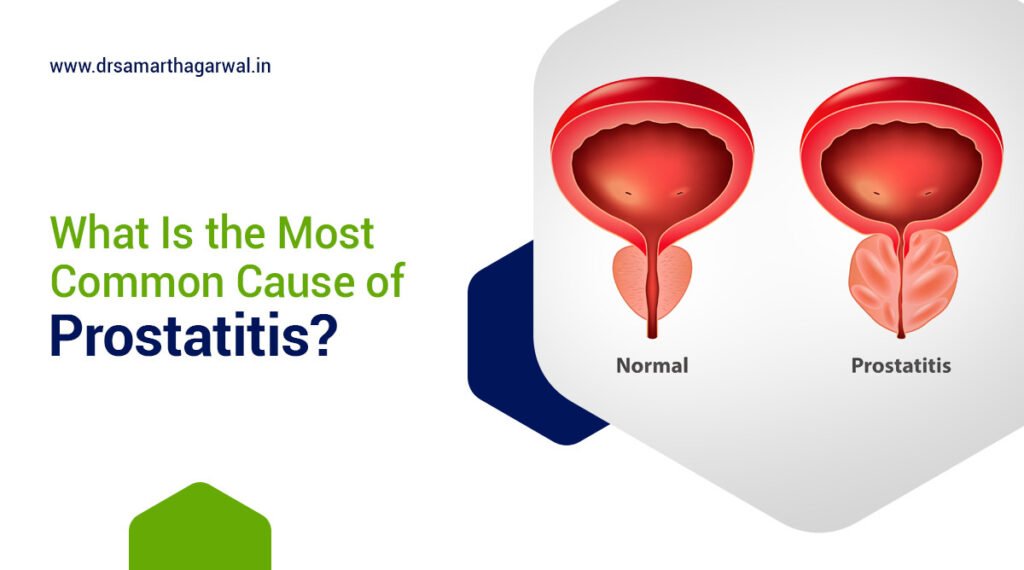
Acute bacterial prostatitis represents a severe infection of the prostate gland caused by bacterial pathogens. This condition manifests as a sudden inflammation of the prostate tissue, requiring prompt medical intervention due to its potential complications. The infection typically stems from urinary tract infections or bacteria entering the prostate through the bloodstream.
What is the Function of the Prostate Gland?
The prostate gland produces seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. This walnut-sized gland surrounds the urethra at the base of the bladder and secretes proteins, enzymes, and citric acid critical for sperm vitality and reproductive function. The prostate contains muscular tissue that helps propel semen during ejaculation, maintaining reproductive health and facilitating proper urinary flow through the urethra.
How is Acute Bacterial Prostatitis Defined?
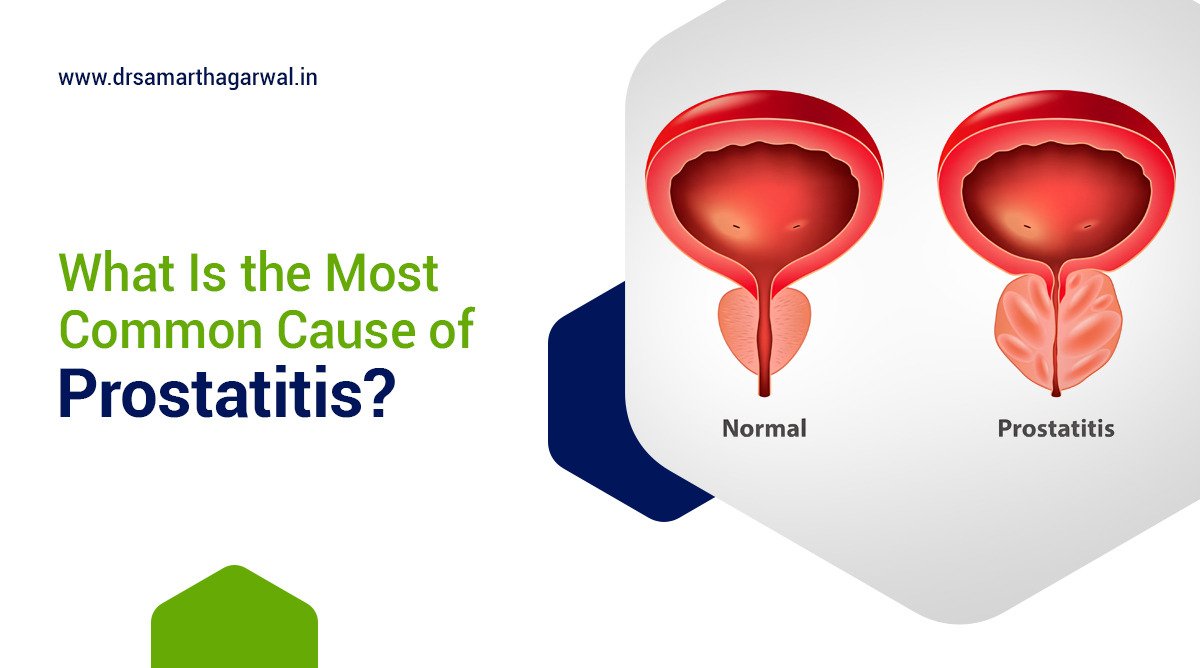
Acute bacterial prostatitis defines a sudden bacterial infection of the prostate gland characterized by severe inflammation and systemic symptoms. This condition represents one of four types of prostatitis, distinguished by its rapid onset and severe presentation. Pathogenic bacteria invade prostate tissue, trigger inflammatory responses, and create an infectious environment that disrupts normal prostate function and causes significant urinary and systemic symptoms requiring immediate treatment.
What are the Common Causes of Acute Bacterial Prostatitis?
Acute bacterial prostatitis develops from specific bacterial sources and transmission routes. The primary causes include:
- Escherichia coli bacteria from intestinal flora
- Urinary tract infections ascending to the prostate
- Transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy complications
- Sexually transmitted infections including chlamydia and gonorrhea
- Urinary catheterization introducing bacteria
- Urethral strictures or blockages impeding normal urine flow
- Rectal bacteria entering the prostate during anal intercourse
- Hematogenous spread of bacteria through bloodstream
- Immune system compromisation facilitating bacterial growth
- Prostate massage introducing bacteria into the gland
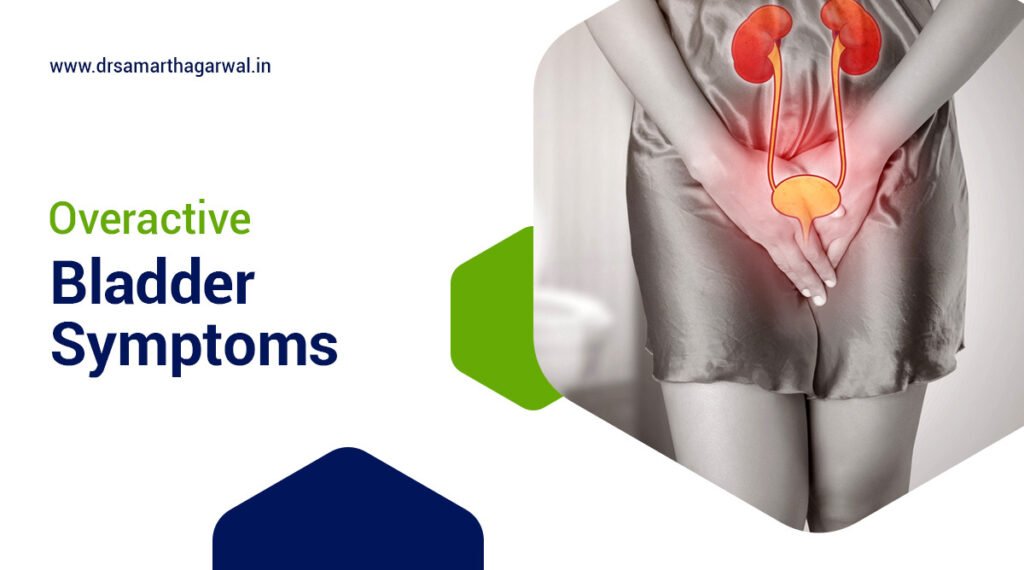
How Can Symptoms of Acute Bacterial Prostatitis be Recognized?
Acute bacterial prostatitis presents with distinctive symptoms requiring immediate medical attention. The symptoms include:
- Sudden high fever exceeding 101°F (38.3°C) can be a symptom of acute prostatitis.
- Severe chills and rigors
- Intense pelvic and lower back pain
- Painful urination (dysuria)
- Frequent urination, particularly at night
- Urgency to urinate with minimal output
- Difficulty initiating urination
- Symptoms of prostatitis may include cloudy or bloody urine.
- Complete urinary retention requiring catheterization
- Pain during ejaculation
- Rectal pressure or pain
- Painful rectal examination
- Systemic malaise and fatigue
- Joint and muscle aches
- Decreased urinary stream force
- Bladder distention from incomplete emptying
What is the Diagnosis Process for Acute Bacterial Prostatitis?
Acute bacterial prostatitis diagnosis involves comprehensive evaluation protocols to identify the infection and determine its severity. The physician begins with a thorough medical history assessment, documenting urinary symptoms and recent procedures. Physical examination includes gentle rectal examination revealing an extremely tender, swollen prostate. Laboratory tests measure white blood cell counts, C-reactive protein levels, and prostate-specific antigen levels. Urine culture identifies specific bacterial pathogens and antibiotic sensitivities, while blood cultures detect bacteremia. Imaging studies like transrectal ultrasonography visualize prostate abnormalities and potential abscesses, though performed cautiously to avoid spreading infection. Physicians rule out differential diagnoses including prostate cancer, urethritis, and epididymitis through careful symptom evaluation.
What are the harmful effects of overlooking prostatitis?
The harmful effects of overlooking acute bacterial prostatitis include treatment failure, abscess formation, chronic infection, and missed diagnoses of underlying conditions.
According to Yang, Y. (2024). The harmful effects of overlooking acute bacterial prostatitis., Overlooking acute bacterial prostatitis can result in initial treatment failure where inappropriate antibiotic selection may cause organ damage and worsen the patient’s condition. Additionally, inadequate treatment may lead to the formation of prostatic abscesses requiring surgical intervention, transition to chronic bacterial prostatitis necessitating long-term antibiotic treatment, and failure to detect related conditions such as epididymitis or underlying diseases including sexually transmitted infections that may have serious consequences for the patient’s quality of life.
What are the Treatment Approaches for Acute Bacterial Prostatitis?
Acute bacterial prostatitis treatment requires targeted antibiotic therapy and comprehensive symptom management.
According to Yoon, B. I., Han, D.-S., Ha, U.-S., Lee, S.-J., Sohn, D. W., Kim, H. W., Han, C.-H., & Cho, Y.-H. (2013). ‘Clinical courses following acute bacterial prostatitis’, in Prostate International, treatment of acute bacterial prostatitis begins with intravenous antibiotics followed by oral antibiotics for at least 4 weeks. Patients who recovered without chronic complications received longer antibiotic treatment (36.5±10.6 days) compared to those who developed chronic infections (27.5±13.5 days). Hospitalized patients typically received combination therapy with cephalosporin and aminoglycoside, while outpatients were commonly prescribed quinolones.
The treatment protocol includes:
- Intravenous broad-spectrum antibiotics for hospitalized patients
- Fluoroquinolones or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for outpatient cases
- 4-6 week antibiotic course preventing chronic bacterial prostatitis
- Urinary catheterization for severe retention cases
- Alpha-blocker medications relaxing prostate muscles
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs reducing pain and inflammation
- Adequate hydration maintaining urinary flow
- Stool softeners preventing constipation and rectal pressure
- Sitz baths relieving pelvic discomfort
- Prostate abscess drainage when present is crucial in managing severe cases of prostatitis.
- Avoidance of sexual activity during acute phase
- Regular follow-up ensuring complete resolution
- Culture-directed antibiotic adjustment based on sensitivity
- Antipyretics controlling fever
- Pain management with appropriate analgesics
Treatment Approaches for Prostatic Conditions
| Treatment Approach | Specific Interventions | Purpose |
| Antibiotic Therapy | Fluoroquinolones, Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, Cephalosporins | To eliminate bacterial infection |
| Hospitalization may be required for patients with severe acute prostatitis. | IV antibiotics and fluid management are critical in treating acute prostatitis. | To treat severe cases with systemic symptoms |
| Pain Management | NSAIDs, analgesics | To reduce inflammation and alleviate pain |
| Alpha-blockers are often prescribed to alleviate symptoms of prostatitis. | Tamsulosin, Alfuzosin | To relieve urinary symptoms and improve flow |
| Urinary Catheterization | Suprapubic catheter | To manage severe urinary retention |
| Supportive measures are essential in the management of inflammation of the prostate. | Hydration, rest, sitz baths | To promote healing and overall comfort |
| Follow-up Care | PSA testing, urinalysis | To monitor recovery and prevent recurrence of acute prostatitis |
What are the Potential Complications if Acute Bacterial Prostatitis is Left Untreated?
Untreated acute bacterial prostatitis progresses to severe complications affecting urinary and reproductive systems. When infection persists, patients develop chronic bacterial prostatitis with recurring symptoms resistant to treatment. Bacteria spread creates prostatic abscesses requiring surgical drainage and extending hospital stays. Complete urinary retention necessitates emergency catheterization and increases infection risks. Bacteria enter the bloodstream causing life-threatening sepsis with multi-organ dysfunction.
Pelvic floor dysfunction develops from prolonged inflammation, creating chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Ejaculatory duct scarring leads to fertility problems including decreased sperm quality and ejaculatory pain. Repeated inflammation increases prostate cancer risk through cellular damage associated with chronic prostatitis. Urethral strictures form, permanently narrowing the urethra and requiring surgical correction. Kidney damage occurs when infection ascends, potentially causing permanent renal function impairment.
What are the Prevention Strategies for Acute Bacterial Prostatitis?
Acute bacterial prostatitis prevention encompasses targeted strategies addressing infection risk factors. Key prevention measures include:
- Treating urinary tract infections promptly and completely
- Practicing safe sexual behaviors including condom use
- Maintaining adequate hydration supporting regular urination
- Implementing antibiotic prophylaxis before prostate biopsies
- Emptying the bladder completely during urination
- Avoiding prolonged sitting periods causing prostatic congestion
- Practicing proper catheter care when required is essential to prevent acute infection.
- Completing prescribed antibiotic courses fully
- Addressing urinary flow obstructions promptly
- Managing immune system disorders effectively
- Incorporating regular ejaculation promoting prostatic fluid drainage
- Following post-procedure protocols after urological interventions
- Maintaining balanced diet supporting immune function
- Addressing constipation preventing rectal pressure
- Implementing stress reduction techniques decreasing pelvic floor tension
When Should One Seek Medical Attention for Acute Bacterial Prostatitis?
Acute bacterial prostatitis requires immediate medical attention when specific symptoms appear. Seek emergency care for:
- High fever exceeding 101°F (38.3°C) with chills
- Complete inability to urinate despite urgency
- Severe pelvic pain unrelieved by over-the-counter medications
- Blood in urine or semen
- Confusion, disorientation, or extreme weakness indicating sepsis
- Significant lower back pain radiating to legs
- Rapid heart rate and breathing indicating systemic infection
- Inability to sit comfortably due to rectal/perineal pain
- Worsening symptoms of prostatitis despite started antibiotics can indicate treatment failure.
- New symptom development during treatment for acute prostatitis should be closely monitored.
- Testicular pain or swelling suggesting spread of infection
- Persistent symptoms beyond 48 hours of treatment
- Recurrent episodes after completed treatment
- Unusual discharge from urethra
- Development of new neurological symptoms
How Does Acute Bacterial Prostatitis Relate to Other Prostate Conditions?
Acute bacterial prostatitis connects with multiple prostate conditions through related pathophysiology and risk factors.
| Condition | Relationship with Acute Bacterial Prostatitis | Key Differences |
| Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis | Often develops from inadequately treated acute cases | Subtle, recurrent symptoms of prostatitis; more difficult bacterial eradication may occur. |
| Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome | Shares pelvic pain features with acute cases | Non-bacterial inflammation; psychological factors involved; longer duration |
| Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis | Involves prostatic inflammation | No symptoms; found incidentally; lacks bacterial infection |
| Prostate Cancer | Chronic inflammation may elevate cancer risk | Malignant growth; slower progression; different diagnostic markers |
| Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) may coexist with symptoms of prostatitis. | Both may cause urinary symptoms | Non-infectious and gradual growth; typically age-related |
| Prostatodynia | Similar pelvic pain presentation | Muscular pain without infection; normal prostate exam |
| Prostatic Abscess | Acute infection can be a complication of acute bacterial prostatitis. | Localized pus collection; more severe clinical presentation |
| Urethritis | May precede or accompany prostatitis | Inflammation restricted to the urethra; different causative organisms |
| Epididymitis | May coexist with prostatitis | Primarily involves epididymis; includes testicular symptoms |
| Prostatosis | Both acute prostatitis and chronic prostatitis affect prostate function significantly. | Congestion without true infection; generally milder symptoms |
How Can One Live with and Recover from Acute Bacterial Prostatitis?
Acute bacterial prostatitis recovery requires comprehensive management strategies addressing physical and lifestyle factors, including urology referrals. Recovery begins with complete adherence to prescribed antibiotic regimens, and taking medications at consistent times with appropriate food requirements. Patients maintain hydration by drinking 2-3 liters daily, diluting urine, and flushing bacteria. Temporary dietary adjustments eliminate bladder irritants including caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods. Rest promotes healing while gradually increasing physical activity and avoids prolonged sitting.
Warm sitz baths provide symptomatic relief 2-3 times daily. Follow-up appointments monitor treatment effectiveness through symptom assessment and repeat urine cultures. Sexual activity resumes gradually after symptom resolution and physician clearance. Pelvic floor relaxation techniques alleviate tension contributing to pain. Stress management reduces physical tension exacerbating symptoms. Long-term monitoring detects recurrence, with prompt attention to returning symptoms preventing chronic development.
What are the Advances in Research and Treatment for Acute Bacterial Prostatitis?
Acute bacterial prostatitis research advances targeted treatments and diagnostic innovations addressing bacterial resistance. Current research explores bacteria-specific bacteriophage therapy targeting pathogens without disrupting beneficial microbiome populations. Advanced imaging techniques including multiparametric MRI provide enhanced visualization of prostatic abscesses and inflammation patterns. Biomarker development identifies specific inflammatory markers improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment response predictions.
Antibiotic delivery systems utilizing nanoparticle technology enhance penetration into prostate tissue, increasing treatment efficacy. Microbiome analysis examines urinary and prostatic bacterial populations, understanding their role in infection susceptibility. Immunomodulatory treatments regulate excessive inflammatory responses in acute prostatitis, reducing tissue damage. Genetic susceptibility studies identify predisposing factors explaining recurrent infections. Novel antimicrobial peptides derived from natural sources combat resistant bacteria strains. Personalized treatment algorithms incorporate patient factors, bacterial profiles, and resistance patterns optimizing therapeutic approaches for individual cases.

Contact Dr. Samarth Agarwal if you have any questions or concerns about your Urinary health!